- 制造厂商:TI
- 产品类别:接口
- 技术类目:其他接口
- 功能描述:LVDS 发送器平板显示器 (85MHz)
- 点击这里打开及下载DS90C385A的技术文档资料
- TI代理渠道,提供当日发货、严格的质量标准,满足您的目标价格

The DS90C385A is a pin to pin compatible replacement for DS90C383, DS90C383A and DS90C385. The DS90C385A has additional features and improvements making it an ideal replacement for DS90C383, DS90C383A and DS90C385. family of LVDS Transmitters.
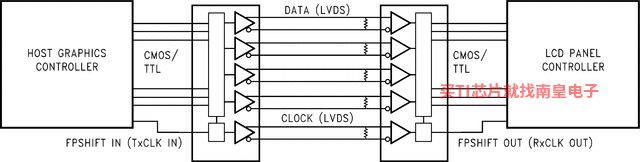
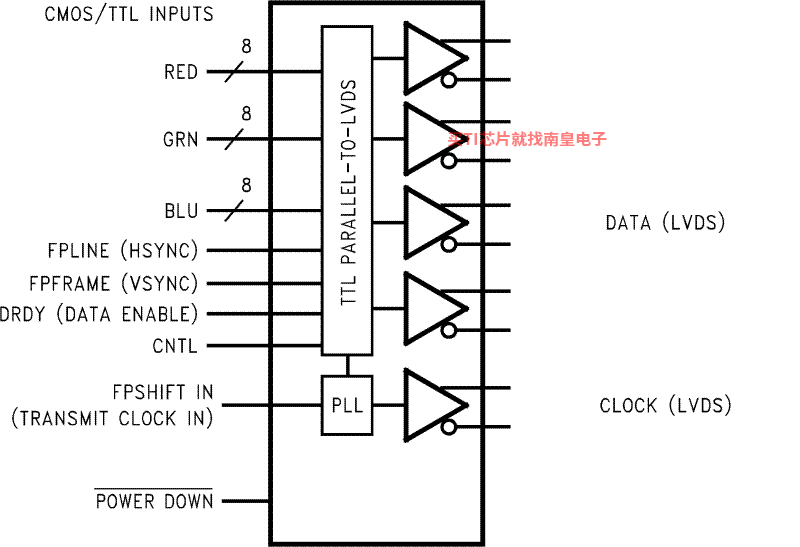
The DS90C385A transmitter converts 28 bits of LVCMOS/LVTTL data into four LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling) data streams. A phase-locked transmit clock is transmitted in parallel with the data streams over the fifth LVDS link. Every cycle of the transmit clock 28 bits of input data are sampled and transmitted. At a transmit clock frequency of 87.5 MHz, 24 bits of RGB data and 3 bits of LCD timing and control data (FPLINE, FPFRAME, DRDY) are transmitted at a rate of 612.5Mbps per LVDS data channel. Using a 87.5 MHz clock, the data throughput is 306.25Mbytes/sec. This transmitter can be programmed for Rising edge strobe or Falling edge strobe through a dedicated pin. A Rising edge or Falling edge strobe transmitter will interoperate with a Falling edge strobe FPDLink Receiver without any translation logic.
This chipset is an ideal means to solve EMI and cable size problems associated with wide, high-speed TTL interfaces with added Spread Spectrum Clocking support.
- Pin-to-Pin Compatible to DS90C383, DS90C383A and DS90C385
- No Special Start-Up Sequence Required between Clock/Data and /PD Pins. Input Signals (Clock and Data) can be Applied Either Before or After the Device is Powered.
- Support Spread Spectrum Clocking up to 100kHz Frequency Modulation and Deviations of ±2.5% Center Spread or -5% Down Spread
- “Input Clock Detection" Feature Will Pull All LVDS Pairs to Logic Low When Input Clock is Missing and When /PD Pin is Logic High
- 18 to 87.5 MHz Shift Clock Support
- Tx Power Consumption < 147 mW (typ) at 87.5MHz Grayscale
- Tx Power-Down Mode < 60 μW (typ)
- Supports VGA, SVGA, XGA, SXGA(Dual Pixel), SXGA+(Dual Pixel), UXGA(Dual Pixel).
- Narrow Bus Reduces Cable Size and Cost
- Up to 2.45 Gbps Throughput
- Up to 306.25Megabyte/sec Bandwidth
- 345 mV (typ) Swing LVDS Devices for Low EMI
- PLL Requires No External Components
- Compliant to TIA/EIA-644 LVDS standard
- Low Profile 56-lead TSSOP Package
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
- Operating temperature range (C)
- -10 to 70
DS90C385A的完整型号有:DS90C385AMT/NOPB、DS90C385AMTX/NOPB,以下是这些产品的关键参数及官网采购报价:
DS90C385AMT/NOPB,工作温度:-10 to 70,封装:TSSOP (DGG)-56,包装数量MPQ:34个,MSL 等级/回流焊峰值温度:Level-2-260C-1 YEAR,引脚镀层/焊球材料:SN,TI官网DS90C385AMT/NOPB的批量USD价格:1.896(1000+)
DS90C385AMTX/NOPB,工作温度:-10 to 70,封装:TSSOP (DGG)-56,包装数量MPQ:1000个,MSL 等级/回流焊峰值温度:Level-2-260C-1 YEAR,引脚镀层/焊球材料:SN,TI官网DS90C385AMTX/NOPB的批量USD价格:1.58(1000+)

FLINK3V8BT-85 — 用于 FPD 链接系列串行器和解串器 LVDS 器件的评估套件
FPD-Link evaluation kit contains a Transmitter (Tx) board, a Receiver (Rx) board along with interfacing cables. This kit will demonstrate the chipsets interfacing from test equipment or a graphics controller using Low Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS) to a receiver board.
The Transmitter board (...)
DS90C385A IBIS Model
PSpice for TI 可提供帮助评估模拟电路功能的设计和仿真环境。此功能齐全的设计和仿真套件使用 Cadence 的模拟分析引擎。PSpice for TI 可免费使用,包括业内超大的模型库之一,涵盖我们的模拟和电源产品系列以及精选的模拟行为模型。借助?PSpice for TI 的设计和仿真环境及其内置的模型库,您可对复杂的混合信号设计进行仿真。创建完整的终端设备设计和原型解决方案,然后再进行布局和制造,可缩短产品上市时间并降低开发成本。
在?PSpice for TI 设计和仿真工具中,您可以搜索 TI (...)
TINA-TI — 基于 SPICE 的模拟仿真程序
TINA-TI 提供了 SPICE 所有的传统直流、瞬态和频域分析以及更多。TINA 具有广泛的后处理功能,允许您按照希望的方式设置结果的格式。虚拟仪器允许您选择输入波形、探针电路节点电压和波形。TINA 的原理图捕获非常直观 - 真正的“快速入门”。TINA-TI 安装需要大约 500MB。直接安装,如果想卸载也很容易。我们相信您肯定会爱不释手。
TINA 是德州仪器 (TI) 专有的 DesignSoft 产品。该免费版本具有完整的功能,但不支持完整版 TINA 所提供的某些其他功能。
如需获取可用 TINA-TI 模型的完整列表,请参阅:SpiceRack - 完整列表
需要 HSpice (...)
TIDA-010013 — 适用于 Sitara 处理器的 RGB 转 OLDI/LVDS 显示桥接参考设计
Higher resolution displays are now in larger demand than ever before. This results in a higher pixel clock which can lead to challenges such as high EMI emission and noise immunity. As a result, the video interface now transitions from a traditional RGB to LVDS video interface. As microprocessors (...)